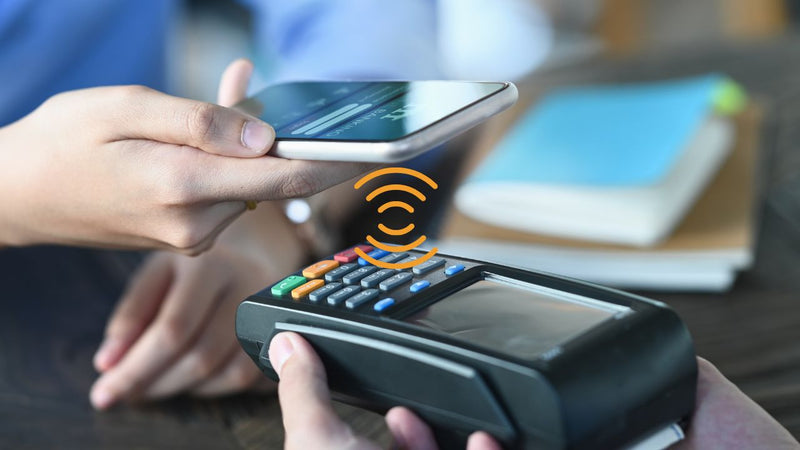
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows devices to exchange data securely with just a tap or close-range interaction. In the Internet of Things (IoT), NFC is increasingly being recognized as a powerful tool for simplifying IoT connectivity with NFC technology across a wide range of use cases, both in consumer smart home environments and in industrial operations.
With the number of connected devices growing rapidly, efficient and secure commissioning, pairing, and control methods are essential. NFC enables secure and seamless IoT device pairing using NFC, supports NFC-enabled authentication for IoT security, and provides an intuitive way to interact with devices that may lack traditional user interfaces.
Commissioning Devices
One of the persistent challenges in IoT deployment is the lack of a standardized process for commissioning new devices. Manufacturers often use their own proprietary setup methods, which can make adding devices to a network time-consuming and inconsistent. This is especially frustrating when dealing with devices that lack displays or input controls.
NFC offers a universal approach. With a single tap, network credentials, encryption keys, and configuration settings can be transferred directly to the device. This eliminates the need for complicated pairing steps or manually entering long strings of data.
In a smart home, NFC could allow a user to add a new security camera or appliance in seconds without navigating menus or downloading extra configuration software. In industrial environments, such as a manufacturing plant or logistics hub, technicians can walk down a production line and commission dozens of wireless sensors quickly and consistently, reducing downtime and human error.
By providing a standardized mechanism for adding devices to a network, NFC ensures that onboarding is fast, repeatable, and secure across different device types and brands.

NFC-Based Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Pairing
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are the most common connectivity options for IoT devices, but the traditional pairing process can be slow and error-prone. Manually finding network names, typing in passwords, or waiting through Bluetooth discovery can be inefficient, especially when dozens or hundreds of devices need to be connected.
The NFC Forum has worked closely with both the Bluetooth SIG and the Wi-Fi Alliance to create faster, more secure pairing processes. With NFC, devices can be configured and paired instantly by tapping them together or against an NFC tag preloaded with the correct credentials.
In a smart home, this could mean instantly connecting a new thermostat or lighting hub to the correct Wi-Fi network without entering a password. In an industrial setting, it might involve quickly pairing a Bluetooth-enabled diagnostic tool with a technician’s tablet or connecting a temporary wireless monitor in a high-noise area where voice or manual entry is impractical.
This is a prime example of integrating NFC for touch-based IoT control, replacing multi-step pairing procedures with a fast, reliable, and secure method.
Headless Device Commissioning
“Headless” devices, those without displays, buttons, or built-in interfaces, are common in both residential and industrial IoT. While they often deliver valuable functionality, they can be difficult to configure without specialized tools or cumbersome workarounds.
NFC streamlines this process. A device can be commissioned simply by tapping it against an NFC tag containing network credentials or configuration data. Once the connection is established, the tag can erase its stored keys to prevent unauthorized access, supporting NFC-enabled authentication for IoT security.
In smart home applications, this could simplify the setup of embedded lighting controllers or in-wall switches. In industrial contexts, it could be used for commissioning embedded sensors inside machinery without needing to dismantle equipment or run special wiring.
Controlling a Device with No User Interface
Even after deployment, many IoT devices lack built-in controls. They may be embedded in walls, sealed for environmental protection, or located in hard-to-reach areas. NFC enables secure, contactless interactions for these devices, both for input (provisioning or reconfiguring settings) and output (retrieving diagnostic data or system status).
Examples include:
-
Smart home: Adjusting an irrigation controller or lighting system by tapping a smartphone to the device.
-
Industrial IoT: Pulling maintenance logs from a vibration sensor on a conveyor belt or initiating a calibration routine on a remote monitoring device.
By enhancing IoT user experience with contactless communication, NFC makes it easier to interact with devices on-site without needing additional control hardware or complex remote access systems.
Access Control Across Environments
Security is a top priority in any IoT deployment. NFC can replace mechanical keys and manual lock systems with secure, digital access control. Credentials can be stored on smart cards, fobs, or mobile devices, allowing instant permission updates and detailed entry logs.
-
In residential environments, property managers can issue or revoke access for tenants instantly, send virtual keys to visitors, and track who enters or exits a building.
-
In industrial environments, NFC can control access to equipment, server rooms, or hazardous work zones, ensuring only authorized personnel can make adjustments or retrieve data.
NFC-based access control is flexible, cost-effective, and highly secure, making it suitable for both small deployments and large-scale facilities.
Unlocking NFC’s Full Potential
The versatility of NFC means it can address multiple IoT challenges at once:
-
Commissioning devices without UIs or with complex setup requirements
-
Pairing devices to networks quickly without manual entry
-
Authenticating users and preventing unauthorized access
-
Controlling and updating devices in the field without needing physical interfaces
Whether used in a smart home, a commercial building, or an industrial facility, IoT NFC offers a low-cost, secure, and user-friendly solution for device connectivity and management. From simplifying IoT connectivity with NFC technology to enabling integrating NFC for touch-based IoT control, NFC reduces friction and increases reliability in connected systems.
At Grid Connect, we help organizations implement NFC IoT applications that make deployments faster, safer, and more efficient, ensuring that connected devices deliver maximum value over their lifecycle.